We’re now at the final article in our series about choosing the best product sourcing methods for your ecommerce store. If you’ve been following along, you know we’ve already covered the differences between dropshipping and print on demand, Amazon FBA, and wholesale. Now, it’s dropshipping and private label turn.
So, which model is the right fit for you? Both models allow you to start an online business without a physical storefront, but they offer different levels of control, branding, profit potential, and complexity.
Let’s break down the key differences, along with the pros and cons of each, to help you make the best decision for your business.
Table of Contents
What is dropshipping?
As usual, we’ll start by explaining a bit about what dropshipping involves. Now, dropshipping is an ecommerce business model where you sell products online without handling the inventory or shipping. Instead, you partner with suppliers who fulfill the orders on your behalf. You act as the middleman, focusing on marketing and customer service while the supplier takes care of product storage and delivery.
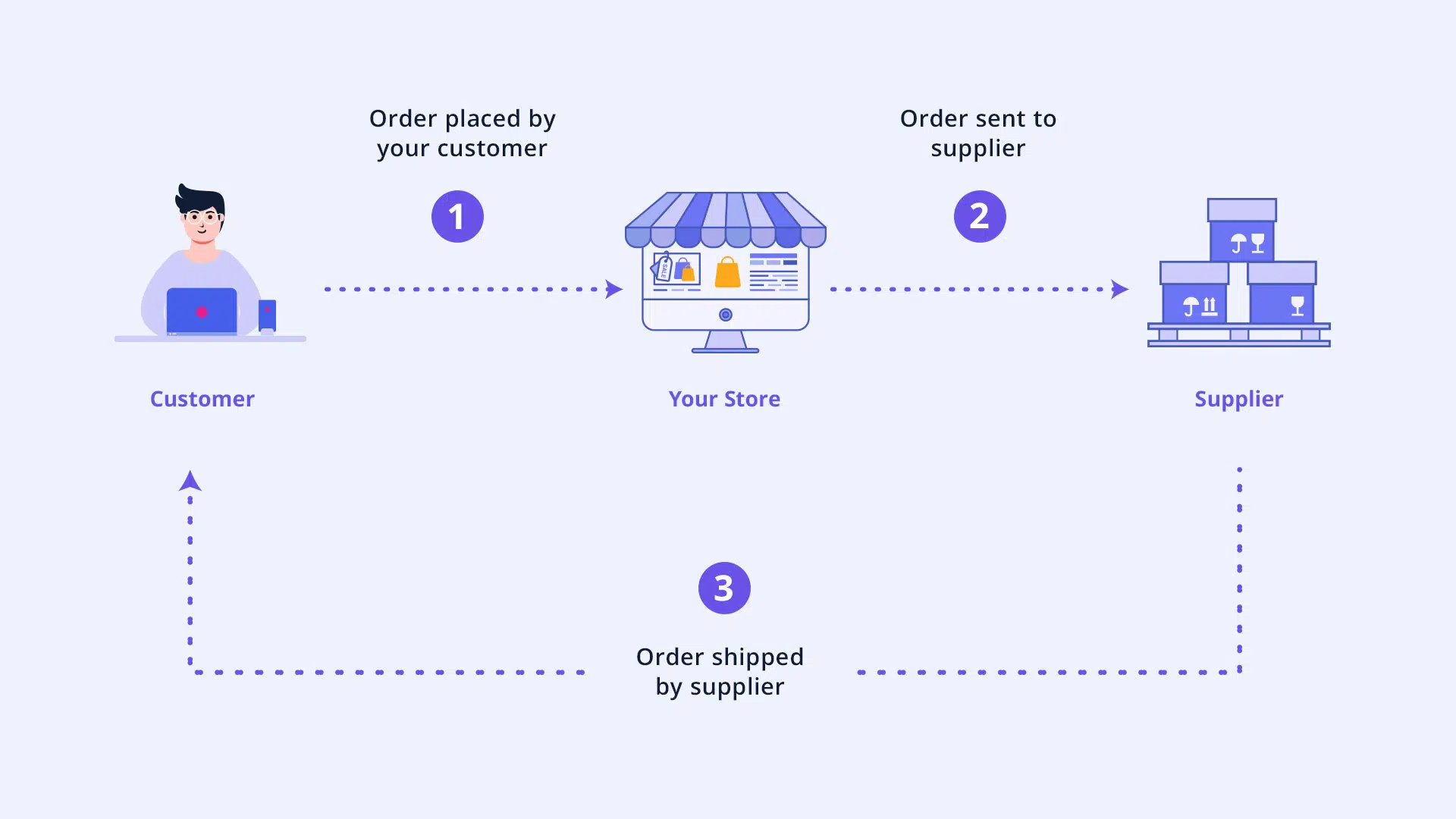
How dropshipping works
- A customer places an order on your online store.
- You forward the order to your dropshipping supplier.
- The supplier ships the product directly to the customer.
- You keep the profit from the difference between the retail price you set and the wholesale price from the supplier.
What is private labeling?
Private labeling, on the other hand, involves working with manufacturers to produce and brand products under your own label. With the private label model, you get greater control over the product, branding, and packaging, but you also take on inventory management, production, and fulfillment responsibilities.
How private labeling works
- You partner with a manufacturer to produce customized products under your brand name.
- You buy products in bulk from the manufacturer.
- You store and manage your inventory, either in your own warehouse or through a fulfillment service.
- When an order is placed, you (or a third-party fulfillment center) ship the product to the customer.
Pros and cons of dropshipping
Pros of dropshipping
- Low startup costs: Since you don’t have to invest in inventory or manage a warehouse, the upfront costs are minimal. You only pay for products once a customer has made a purchase.
- Easy to get started: Dropshipping platforms like Shopify and AppScenic make it easy to set up an online store and start selling within days.
- No inventory management: Suppliers handle all inventory and fulfillment, leaving you free to focus on marketing, customer service, and growing your brand.
- Wide product selection: You can test a wide range of products and change quickly if one product doesn’t sell well. This flexibility is ideal if you want to experiment with different niches.
Cons of dropshipping
- Lower profit margins: Since you’re essentially buying products from a third-party supplier and adding your markup, dropshipping profit margins tend to be thinner than with other ecommerce models like the private label.
- Less control: You rely on your suppliers for product quality, packaging, and shipping times. If a supplier fails to meet expectations, it reflects poorly on your brand.
- Limited branding: With dropshipping, you don’t have much control over product customization or branding. If you don’t invest time and resources in your branding, your dropshipping store could look similar to others selling the same products, making it harder to stand out.
- Higher competition: Because the barriers to entry are low, dropshipping tends to attract a lot of competition. This means you’ll need to work harder to differentiate your store and drive traffic to your site.
Pros and cons of private labeling
Pros of private labeling
- Brand control: With private labeling, you have full control over your branding and product design. This gives you the opportunity to create a unique, differentiated brand that customers can’t find anywhere else.
- Higher profit margins: Since you’re creating your own branded products, you can command higher prices and enjoy bigger profit margins compared to dropshipping.
- Customer loyalty: By offering branded, customized products, you have a better chance of building a loyal customer base that comes back for repeat purchases.
- Product quality control: You work directly with manufacturers, so you have more control over the quality and design of your products, which can lead to better customer satisfaction.
Cons of private labeling
- Higher startup costs: Private labeling requires a significant upfront investment for product design, manufacturing, and inventory management. You’ll need to buy products in bulk, which could lead to overstock or wasted inventory if sales don’t go as planned.
- Inventory management: Unlike dropshipping, private labeling requires you to store and manage inventory, which adds complexity and costs. You may need to invest in a warehouse or use a third-party logistics (3PL) service to handle fulfillment.
- Longer time to launch: Private labeling involves working with manufacturers to develop a custom product, which takes time. There are also additional steps like product testing, packaging design, and ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
- Risk of unsold inventory: Since you’re buying products in bulk, there’s always the risk of being stuck with unsold inventory if demand for the product drops or changes in consumer preferences occur.

Key differences between dropshipping and private labeling
1. Control over product and branding
With dropshipping, you’re limited to selling products that are already available through suppliers. You don’t have much control over product design, packaging, or branding.
In contrast, private labeling allows you to create and sell unique, branded products. If building a strong brand is your goal, private labeling offers more flexibility and customization.
2. Upfront costs
Dropshipping requires very little upfront investment since you only pay for products once they’ve been sold.
Private labeling, on the other hand, involves buying inventory upfront, which can require a larger initial investment.
3. Profit margins
Profit margins are typically lower in dropshipping because you’re reselling third-party products.
With private labeling, you can set your own prices and enjoy higher margins, but you also take on more financial risk by managing inventory and fulfillment.
4. Speed to market
Dropshipping allows you to start selling quickly. You can test products immediately and switch suppliers if something isn’t working.
Private labeling takes more time to get started because you need to design the product, work with manufacturers, and ensure product quality.
5. Risk and inventory management
One of the biggest advantages of dropshipping is that you don’t need to handle inventory.
Private labeling, on the other hand, involves inventory management, which adds logistical complexity and the risk of unsold stock.
Which model should you choose?
Choosing between dropshipping and private label depends on your goals, budget, and level of risk tolerance. Dropshipping is ideal for entrepreneurs who want to start with low upfront costs, minimal risk, and no need to manage inventory. It’s perfect for those looking to experiment with different products or test multiple niches quickly.
Private labeling, on the other hand, is better suited for those who want to build a long-term brand and enjoy higher profit margins. It’s ideal if you’re ready to invest in product development, have more control over your supply chain, and are willing to take on the complexities of inventory management.
Conclusion
Both dropshipping and private labeling offer promising opportunities for anyone who wants to enter the ecommerce world. Dropshipping provides a flexible, low-risk way to enter the market, while private labeling offers the potential for higher profits and stronger brand recognition.
By understanding the pros, cons, and key differences between the two models, you can choose the path that best aligns with your business goals, budget, and long-term vision.